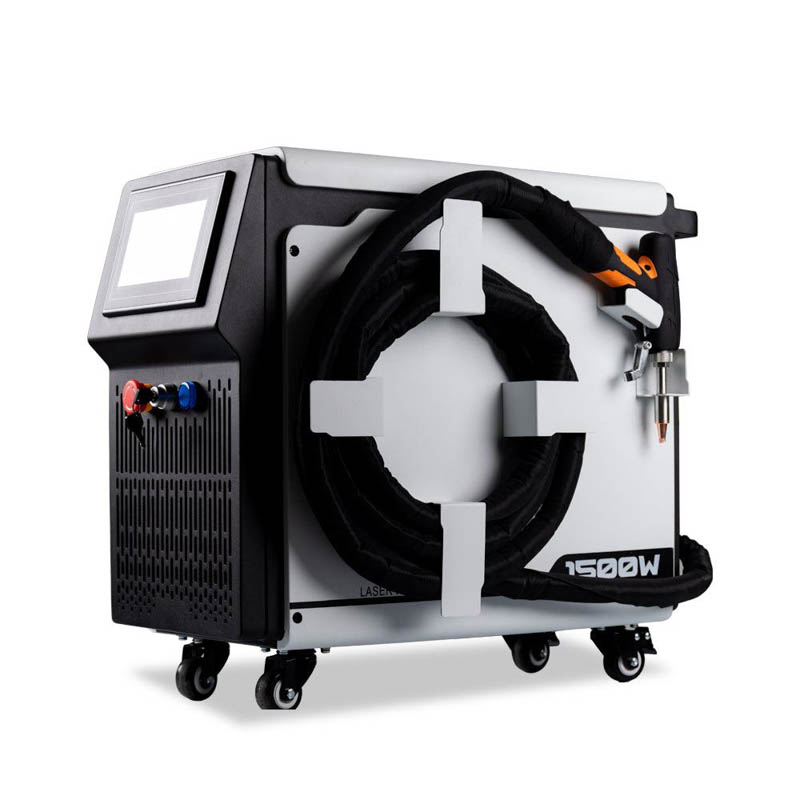
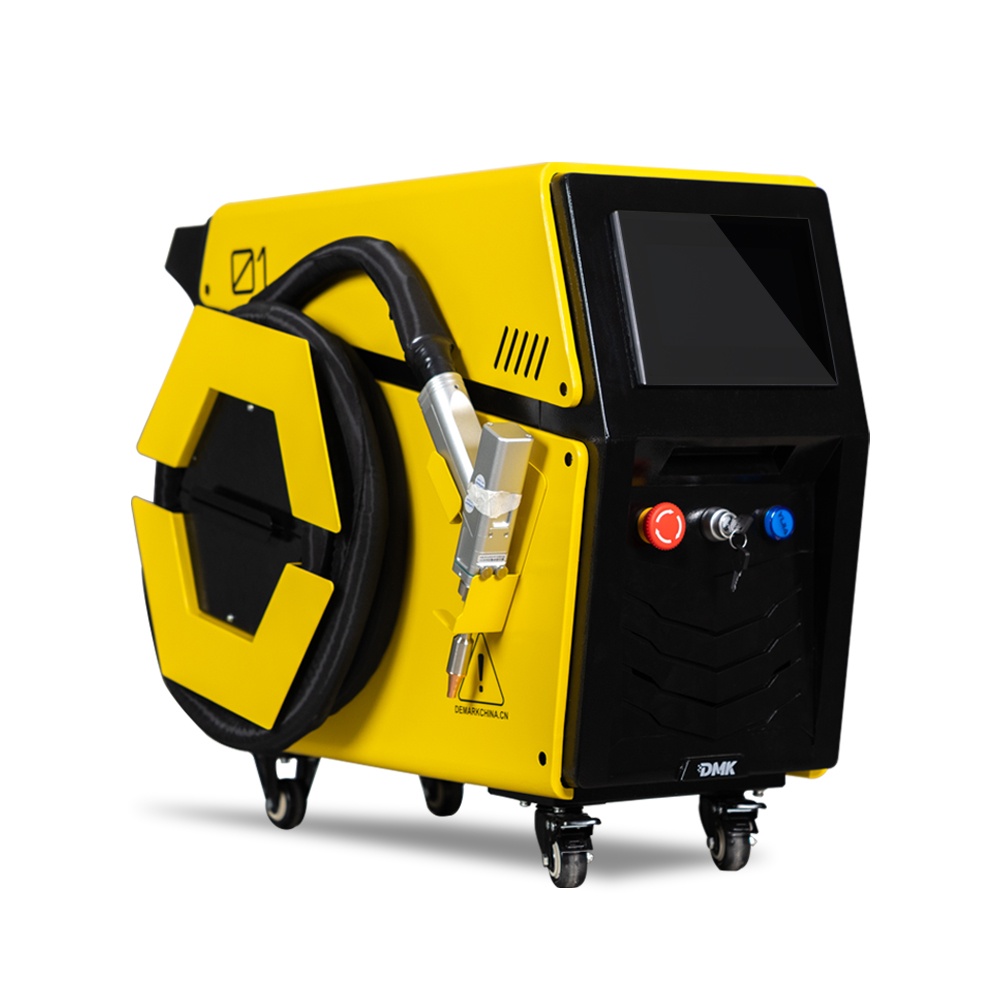
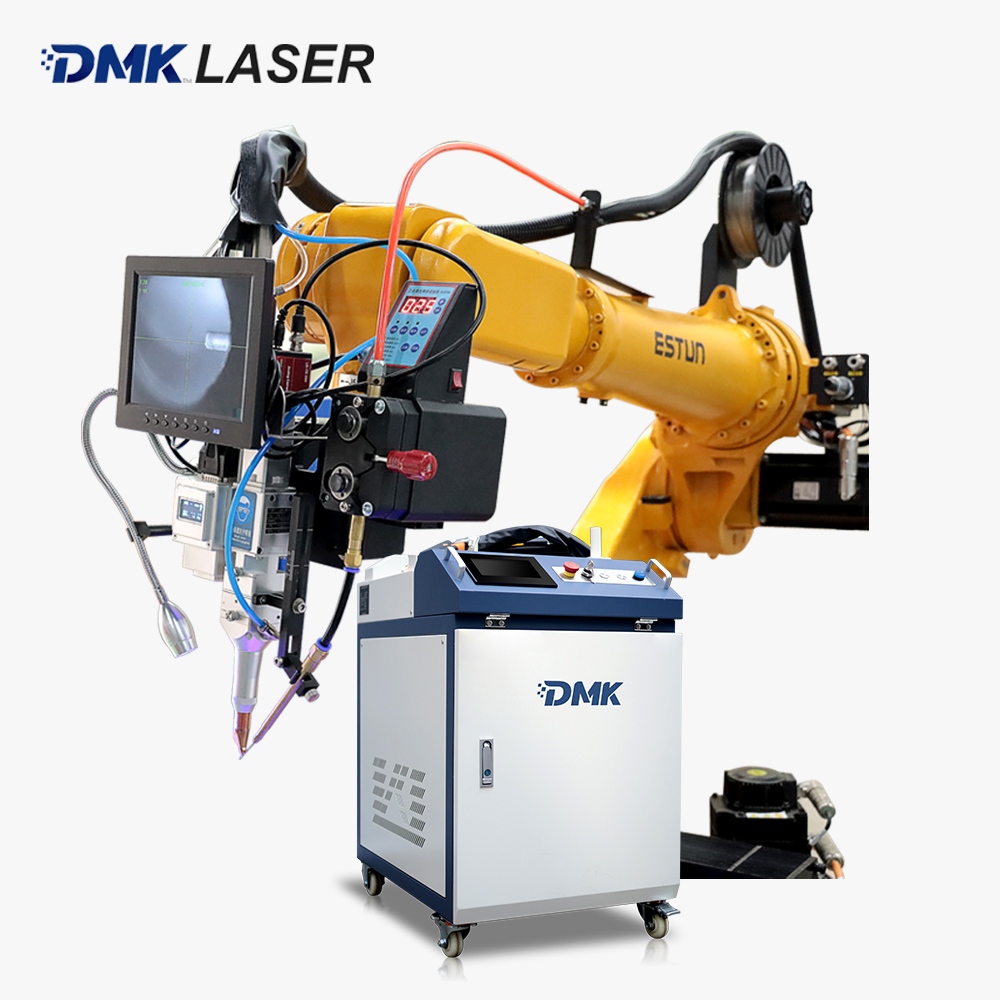
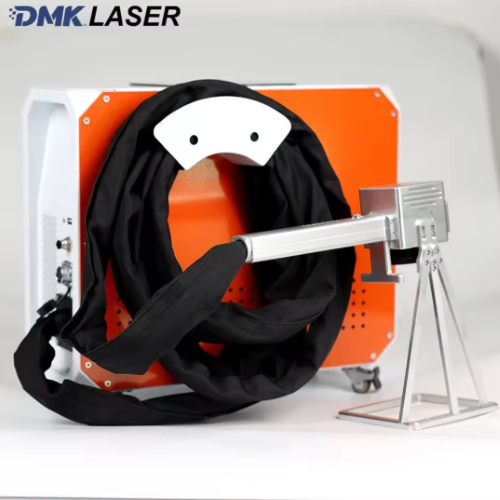
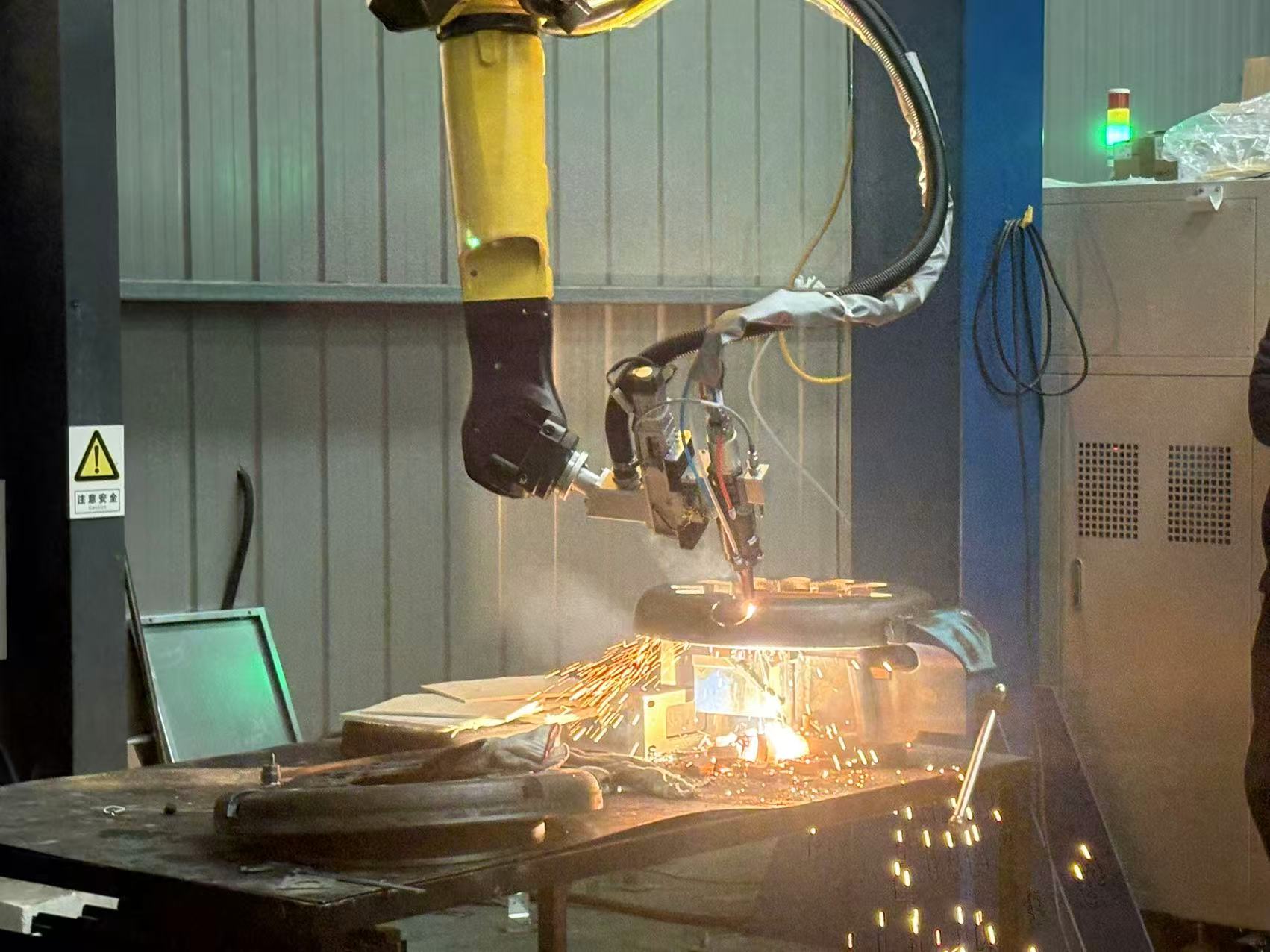
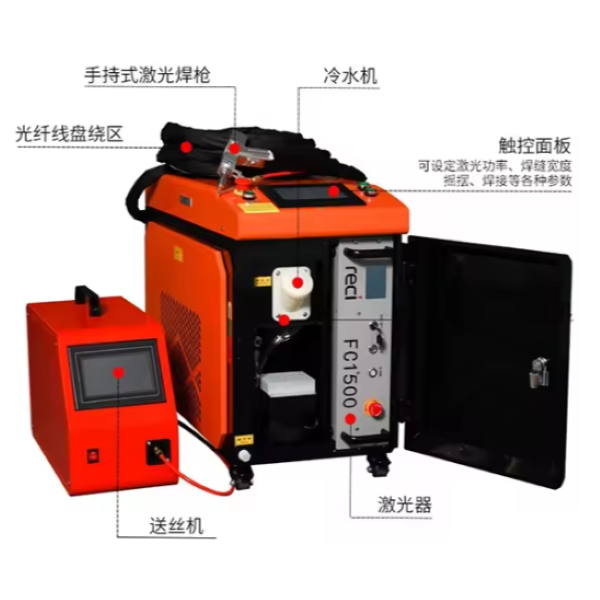
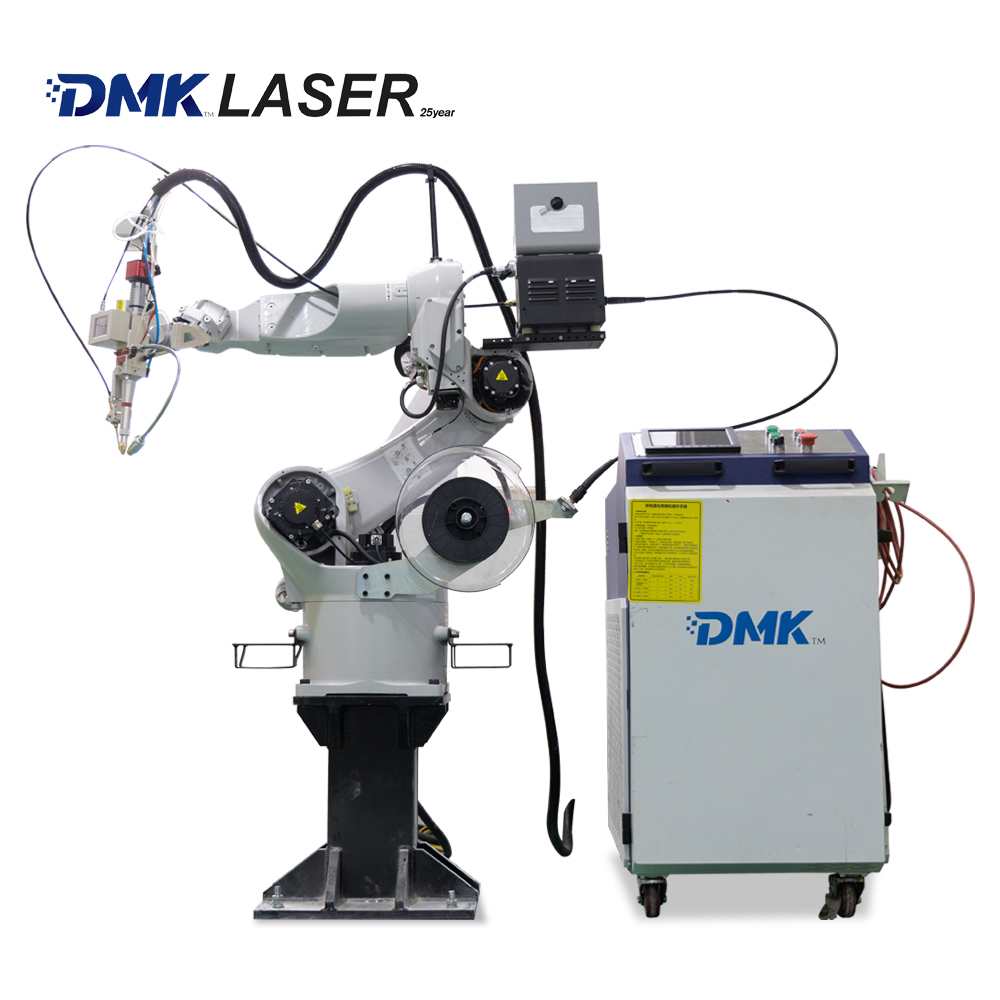
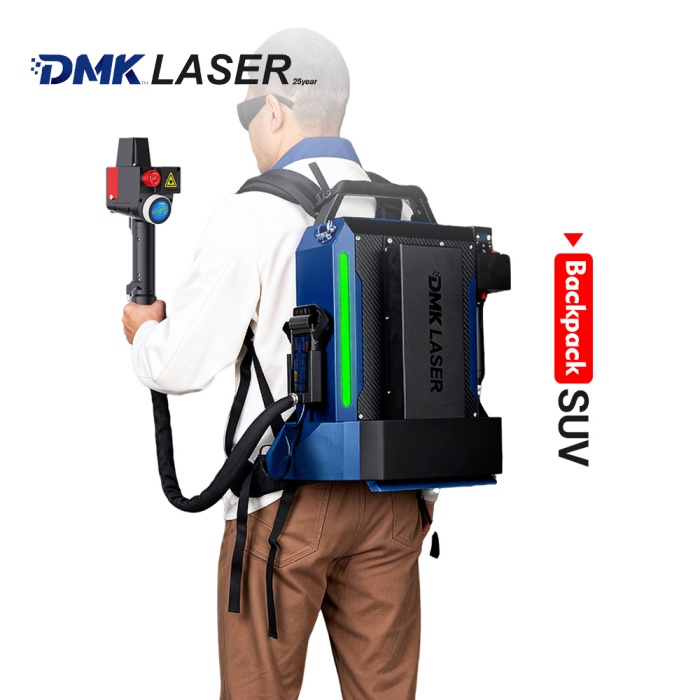
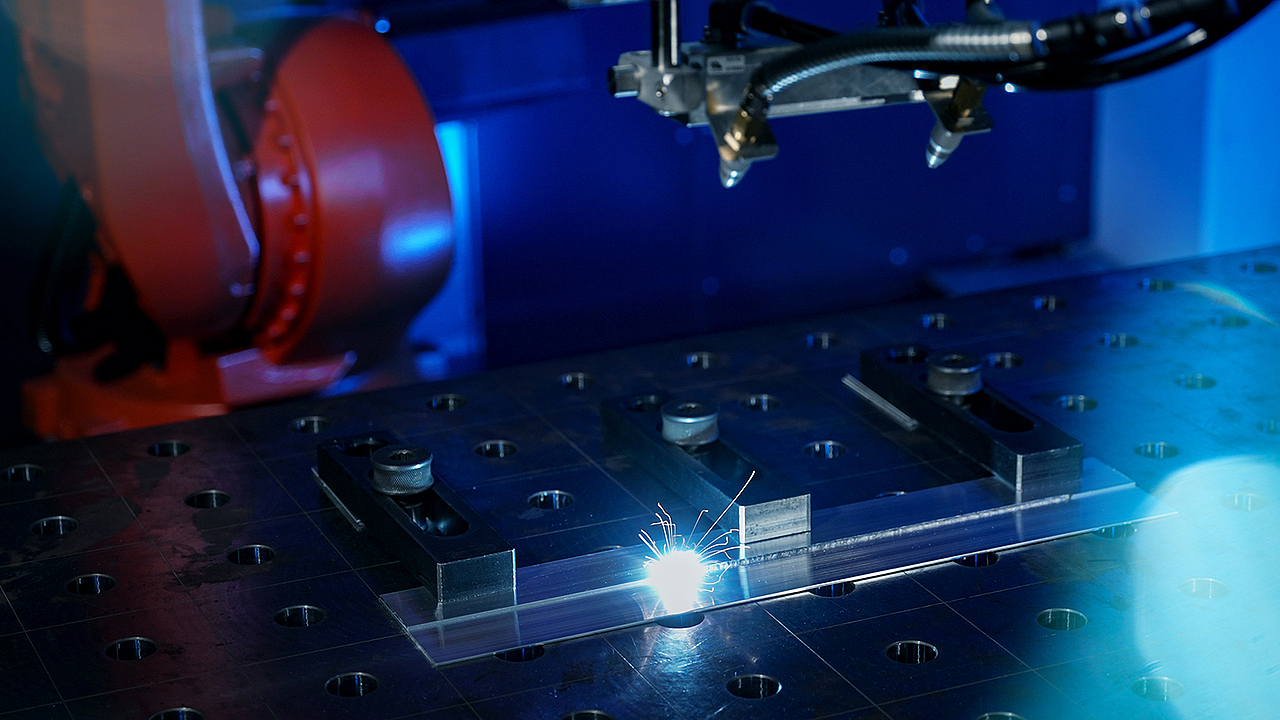
As the core component of most electric vehicles, prismatic battery packs must withstand thousands of charge-discharge cycles, extreme temperatures, and continuous vibrations. Their thin aluminum and copper tabs are highly vulnerable to damage, but modern
laser welding technology can complete precise fusion in just 100 milliseconds. It protects the sensitive chemical components inside the battery while enabling automated systems to perform dozens of high-quality welds per minute. This article details the optimal industrial welding solutions for prismatic batteries, revealing how fiber laser technology makes batteries safer, more durable, and ready for large-scale production.
I. Fiber Laser Welding: The Industry Preferred Choice for Prismatic Battery Welding
In the field of prismatic battery welding, fiber laser systems have comprehensively surpassed traditional solutions such as resistance welding, becoming the mainstream choice in manufacturing workshops worldwide due to their absolute advantages in speed, precision, and reliability. Their core strengths are reflected in five key dimensions:
1. Ultra-High-Speed Welding, Reshaping Production Efficiency
Fiber lasers can complete over 12 connections per second (720 welds per minute), 3-4 times faster than resistance welding. For factories producing 100,000 battery packs annually, this speed advantage can reduce production time by 65%-75%, significantly lowering labor costs and accelerating the return on investment cycle, perfectly adapting to large-scale mass production needs.
2. Micron-Level Precision, Ensuring Welding Consistency
The laser beam can be focused into a spot with a diameter of 0.1 millimeters, with thermal deviation controlled within ±2%. Whether for nickel strip welding or busbar welding, it achieves stable and reliable welding results. This high precision keeps contact resistance below 0.1 milliohms and limits battery capacity loss to less than 0.3%, far superior to the 2%-5% capacity loss of traditional methods, fundamentally eliminating quality randomness.
3. Seamless Automated Integration, Improving Yield
Modern automated battery welding systems integrate lightweight laser heads with vision-guided robots to build a closed-loop real-time monitoring system. The system can detect welding defects in 50 milliseconds, ensuring a first-pass yield of 99.7%-99.9% in high-volume production environments, enabling stable output of high-quality products without manual intervention.
4. Low-Impedance Connections, Optimizing Battery Performance
Low-resistance joints formed by laser welding can increase the overall efficiency of battery packs by 1.2%-1.8%. This technology has been applied in mainstream battery solutions such as Tesla 4680 and CATL Kirin Architecture. Such joints remain stable after more than 5,000 charge-discharge cycles, adding 7-12 miles of range to 100kWh battery packs without modifying battery chemical components.
5. Microscopic Heat-Affected Zone, Protecting Battery Structure
Fiber laser welding completes fusion in just 50-100 milliseconds, narrowing the heat-affected zone to a microscopic range of 0.15-0.3 millimeters. This effectively protects the sensitive separators and electrolytes inside the battery from thermal damage. The final weld strength is typically 15%-25% higher than that of the base material, greatly enhancing the structural stability of the battery pack.
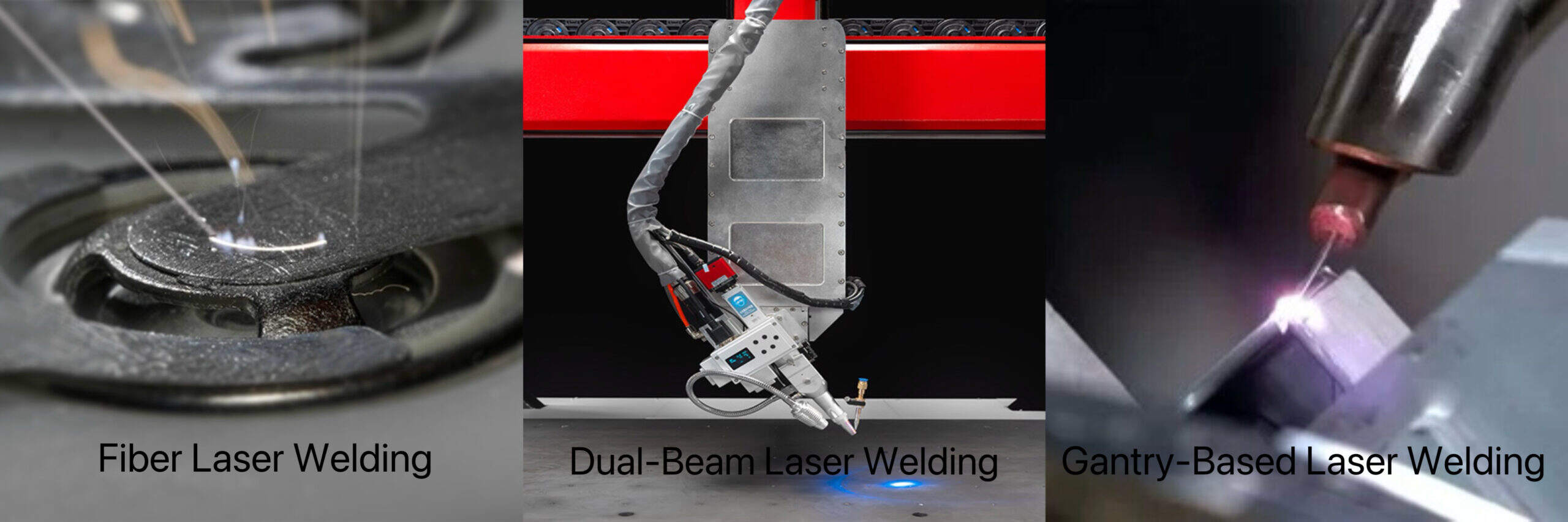
II. Three Core Welding Technologies: Adapting to Different Production Needs
To address the unique structural characteristics and production challenges of prismatic batteries, three types of laser welding technologies have become mainstream choices, which can be flexibly adapted based on battery design, production volume, and quality requirements:
1. Fiber Laser Welding Systems: Balancing Versatility and Precision
This system offers strong material compatibility, capable of welding multiple materials such as copper, aluminum, and nickel on a single platform. It can switch between 0.3-millimeter aluminum sheets and 0.5-millimeter copper busbars via software without hardware replacement. Covering a full power range of 500W-6kW, it features beam quality M²<1.1 and a focused spot size<0.15 millimeters. Its low heat input (15-25J) controls temperature rise at 3 millimeters to less than 15°C, avoiding damage to separators and electrolytes. For dissimilar metal connections, it limits the thickness of the Al-Cu brittle layer to 2-5μm, with resistance remaining less than 0.08mΩ after 8,000 cycles, demonstrating excellent stability.
2. Dual-Beam Laser Technology: Efficient Sealing for Strict Standards
Adopting a 7:3 power distribution between the central beam and annular beam, it ensures deep fusion and leak-free sealing, with an equipment service life of 10-15 years. Equipped with 2-millisecond real-time monitoring, it dynamically compensates for material thickness variations, maintaining the seal width tolerance within ±0.05 millimeters. With a welding speed of 200-400 millimeters per second, it shortens cycle time by 40%-50% and controls porosity below 0.5%; it also reduces the peak welding temperature by 80-120°C, minimizing thermal impact. Its helium leak rate as low as 1×10⁻⁹ mbar·L/s has been adopted by tier-one manufacturers such as LG and Samsung SDI, meeting strict industry standards.
3. Gantry-Based Laser Systems: The Precision Choice for Long-Seam Welding
Optimized for long-seam welding, it achieves a positioning accuracy of ±0.02 millimeters for 200-600 millimeter welds, effectively preventing stress-induced deformation. With a welding speed of 30-80 millimeters per second, it supports single-pass welding of 1.5-2.5 millimeter thick components, ensuring stable deep penetration. The equipment boasts excellent rigidity with a repeatability of ±0.01 millimeters, eliminating vibration errors common in robotic arms; integrated with a high-speed camera of 5,000 frames per second, it detects internal defects in 100 milliseconds, reducing product rejection rates by 0.8%, making it suitable for welding thick-walled components or long seams.
III. Core Technical Adaptation Points for Prismatic Battery Welding
The flat rectangular structure of prismatic batteries presents unique welding challenges. High-quality welding solutions must meet four core requirements: high-speed automation, precise beam delivery, material versatility, and real-time monitoring.
1. High-Speed Automated Integration, Adapting to Mass Production Rhythms
Automated welding systems need to support high-speed production lines of 200-400 units per hour, with feeding mechanisms controlling battery positioning tolerance within ±0.05 millimeters. The vision system completes label scanning in 150 milliseconds, enabling battery cell switching within 2 seconds; online quality inspection analyzes the fusion zone in 120 milliseconds using AI algorithms, ensuring a first-pass yield exceeding 99.5%, perfectly matching the rhythm of large-scale mass production.
2. Precise Beam Delivery, Adapting to Complex Welding Scenarios
The scanning system is equipped with a 8,000-millimeter-per-second galvanometer, expanding dimensional coverage. It can meet both pouch battery welding and busbar-welded battery module needs, with spot sizes adjustable between 0.1-0.8 millimeters. The real-time autofocus function compensates for height variations in 10 milliseconds, ensuring consistency and precision in welding at different positions.
3. Strong Material Versatility, Adapting to Multi-Material Welding
The system features metal recognition capabilities, automatically adjusting power output by 30%-40% for copper/aluminum dissimilar metal joints to optimize welding results. The unique "dual-pulse" process cleans surface coatings before fusion, achieving ultra-low contact resistance and spatter-free welding, stably outputting high-quality joints for both nickel strip welding and dissimilar metal connections.
4. Real-Time Process Monitoring, Ensuring Welding Safety
Multiple sensors work synergistically to complete parameter calibration in 10 milliseconds; a photodiode array monitors plasma emission to ensure welding stability; 20-80kHz ultrasonic detection identifies pore defects larger than 0.1 millimeters, and thermal imaging technology limits the heat-affected zone to within 0.5 millimeters, fully protecting the internal structure of the battery.
IV. Laser Welding vs. Traditional Solutions: Winning with Five Core Advantages
Compared with traditional methods such as resistance welding, laser welding has achieved comprehensive advantages in conductivity, flexibility, mechanical stress, sealing, and process consistency, becoming the industry standard:
1. Superior Conductivity, Enhancing Battery Efficiency
The contact resistance of laser-welded joints is below 0.05 milliohms, 40%-60% lower than resistance spot welding. A 100kWh battery pack can reduce thermal loss by 180-250W, extending range by 8-14 miles per charge without modifying battery chemical components.
2. Non-Contact Welding, Adapting to Complex Structures
Laser welding is a non-contact process; the beam can easily reach recessed areas and narrow gaps that are inaccessible to the bulky electrodes of traditional resistance welding. The beam delivery system maintains 0.02-millimeter precision within a 200-millimeter range, eliminating the need for complex high-pressure clamping systems and adapting to the complex structure of prismatic batteries.
3. Zero Mechanical Stress, Protecting Battery Integrity
Resistance welding requires applying 50-200 psi of pressure, which can easily deform thin-walled batteries or damage internal separators. In contrast, laser welding melts metal through light absorption, with zero mechanical stress throughout the process, preserving the internal structure of the battery and reducing quality rejection rates by 35%-45%.
4. Hermetic Sealing, Extending Battery Lifespan
A moisture content of only 50 ppm can shorten battery cycle life by 30%. The robust fusion zone formed by laser welding has a helium leak rate below 1×10⁻⁹ mbar·L/s, effectively blocking moisture intrusion, protecting electrolyte stability, and extending battery service life to 12-15 years.
5. Stable Processes, Ensuring Batch Quality
Resistance welding electrodes degrade after 5,000-15,000 cycles, while laser optical components can maintain stable operation for 3-5 years with performance deviation less than ±3%. This ensures consistent welding quality between the first and 500,000th battery packs, guaranteeing stability in mass production.
Conclusion
Selecting a suitable welding solution for prismatic batteries is a strategic investment to improve production efficiency, extend product lifespan, and consolidate market competitiveness. Faced with the performance bottlenecks of traditional welding solutions, automated laser systems, with their extremely high precision and speed, significantly reduce thermal loss, improve product yield, and accelerate time-to-market. In an era where battery performance determines market success, upgrading to laser welding technology ensures your production line is future-ready and maintains world-class battery quality. Ready to revolutionize your manufacturing process? Contact us now for a customized process review, and let us tailor the perfect welding solution to meet your production goals.